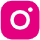
Although a diaphragm fluid pump does not use an electric motor to generate torque and rotation to move or pump fluid, it can still be automated. It is often used to transfer flammable liquids such as chemicals, paints, or other substances that should not be exposed.
Companies that need to pump flammable liquids generally avoid electric motors due to the potential for sparks in liquids such as fuel oils, gases, or other flammable chemicals.
Diaphragm pumps do not use an electric motor, but instead use air to move the piston rod and valve. The basic principle of the diaphragm motor is to use air pressure to move the rod back and forth using two diaphragms.
The air pressure is usually provided by a hose from the compressor and fed to the mechanism that moves the diaphragm. Outlet air is exhausted through the hood.
Although a diaphragm pump only uses air pressure and not an electric motor, it can still be automated.
There are several ways to automate a diaphragm fluid pump, but the basic principle applied is that the pressure of the air supplied to the diaphragm mechanism can be controlled.
The Air Operated Double Diaphragm (AODD) is a positive displacement type positive displacement pump. It does not need to use electricity or an electric motor to generate the torque and force needed to pump liquid or fluid from one point to another.
Instead of a gear driven by torque from an electric motor, a diaphragm pump moves a diaphragm rod through a simple system of air valves.
Diaphragm fluid pumps have two discs. These discs are made of elastic material, which is why the discs are sometimes referred to as flexible diaphragms. Two elastic diaphragms are respectively attached to one end of the diaphragm rod.
The elastic diaphragm consists of two discs and is sometimes referred to as a flexible diaphragm. An elastic diaphragm is attached to each end of the diaphragm rod. Not electricity, but air moves the diaphragm rod.
Whenever the movement of the diaphragm rod approaches the end of its stroke, the control spool located in the middle of the three horizontal rods pushes back and forth.
This reciprocating motion allows air to reciprocate the air distribution valve. By controlling the flow of air into the right or left air chamber, the air distribution lever changes its direction of movement after each stroke.
The pump is designed in such a way that a non-return valve and an elastic diaphragm create a reciprocating motion. Diaphragm pumps, like positive displacement pumps, use this reciprocating motion to move or deliver fluid.
Ball or flap valves control the movement of a fluid or pumped liquids. The differential pressure in the pumped liquid is used to control a ball or flap valve.
Diaphragm fluid pumps are used in a variety of applications including agricultural, manufacturing and industrial processes:
Transfer Material – Used to transfer liquid from one storage container to another. Some examples of the liquids it carries are chemicals and paints.
Supply of liquids to spray equipment and spray lines. It is also used to transfer liquids and fluids to spray equipment or spray lines before they are sprayed onto the target.
Material Removal – Helps remove material that needs to be suctioned or retrieved. If some material is stuck where you don’t want or need it, you can use a diaphragm pump to pull it out and move it to another location.
Diaphragm fluid pumps are useful equipment for pumping flammable liquids that pose a risk to public health and safety. Although it does not use electric motors, its application and some aspects of the input and output process can be automated.
Filed Under: Industry Tagged With: air, diaphragm, diaphragm, electrical, fluid, liquid, motor, displacement, pressure, pump, rod.
Post time: Feb-11-2023